BIM-GIS Integration
Integration of Building Information Modeling (BIM) with Geographic Information Systems (GIS) is increasingly becoming essential in the architecture, engineering, and construction (AEC) industry. GIS is a system designed to capture, store, manipulate, analyze, manage, and present spatial or geographic data. It provides a framework for understanding patterns, relationships, and trends in geographic information.
BIM-GIS integration involves the interoperability between BIM software platforms and GIS software platforms to combine spatial data with building information. The integration enables stakeholders to visualize, analyze, and manage both the physical and geographical aspects of a project in a single environment.
Various software tools and technologies support BIM-GIS integration, including interoperability standards such as Industry Foundation Classes (IFC), Geographic Markup Language (GML), and CityGML. BIM software platforms such as Autodesk Revit and Trimble Tekla can be integrated with GIS software platforms such as Esri ArcGIS and QGIS. BIM-GIS integration has numerous use cases across industries, including urban planning, infrastructure development, environmental management, and facility management. Examples include site selection analysis, environmental impact assessment, transportation planning, and disaster management.
BIM-GIS integration offers significant benefits for stakeholders in the AEC industry by combining spatial data with building information to support better decision-making, planning, and management of projects and assets. Despite challenges, advancements in interoperability standards and technology continue to drive the adoption of BIM-GIS integration in various applications.

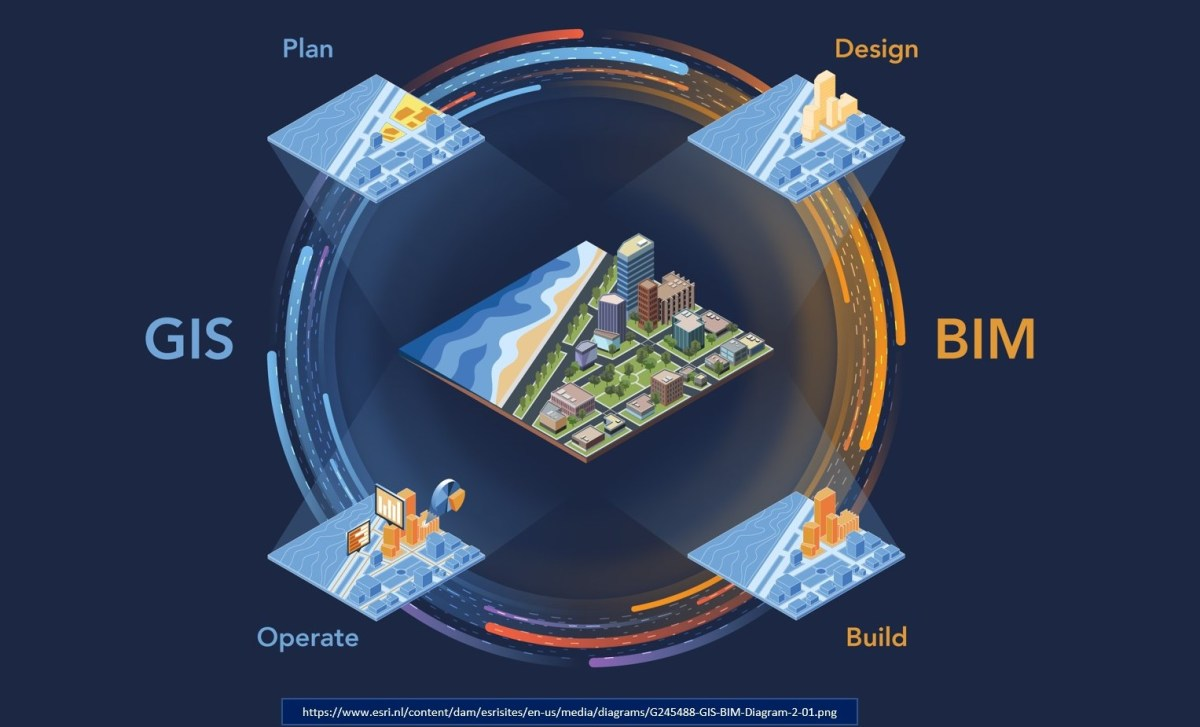
Key Applications & Benefits of BIM–GIS Integration
- Spatial Analysis: GIS provides powerful spatial analysis capabilities, allowing users to analyze and visualize BIM data in relation to geographic features such as terrain, land use, and environmental factors.
- Site Selection: BIM-GIS integration enables better site selection by considering geographic factors such as topography, proximity to amenities, and environmental constraints.
- Facility Management: Integrating BIM with GIS allows for better facility management by linking building information with geographic data such as property boundaries, utility networks, and infrastructure assets.
- Urban Planning: BIM-GIS integration supports urban planning efforts by providing tools for analyzing and simulating the impact of proposed developments on the surrounding environment and infrastructure.
- Emergency Response: GIS can be used to visualize building information in the context of emergency response planning, helping first responders better understand building layouts and access points during emergencies.